Waste to Energy (WtE and EfW)
Waste to Energy
Waste to Energy (WTE) plants, also known as Energy from Waste (EfW), transform non-recyclable waste into electricity, promoting sustainability and reducing landfill use. Through efficient incineration, these plants generate steam to power turbines, producing renewable energy and repurposing excess heat for local use.
Often referred to as energy recovery or combined heat and power plants, WTE facilities are carbon-negative, offering a cleaner alternative to coal-fired plants and landfill disposal. They significantly reduce harmful emissions like nitrogen oxides, sulphur oxides, and particulates, thanks to advanced pollution control technologies like scrubbers and baghouses.
WTE plants are at the forefront of sustainable waste management, delivering renewable energy while combating climate change and ensuring a healthier environment.
Why Monitor Emissions in a Waste to Energy Plant?
Cost savings
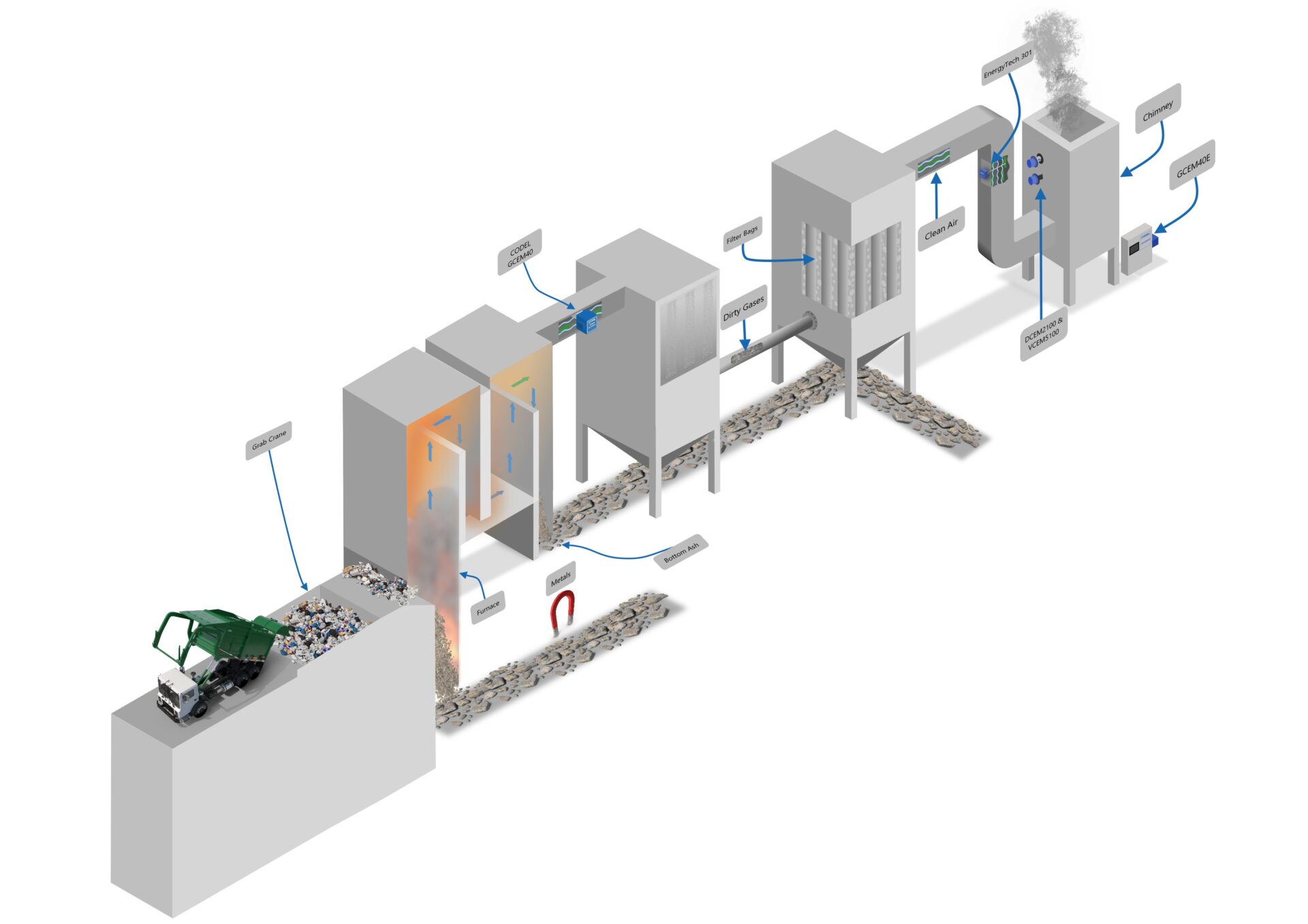
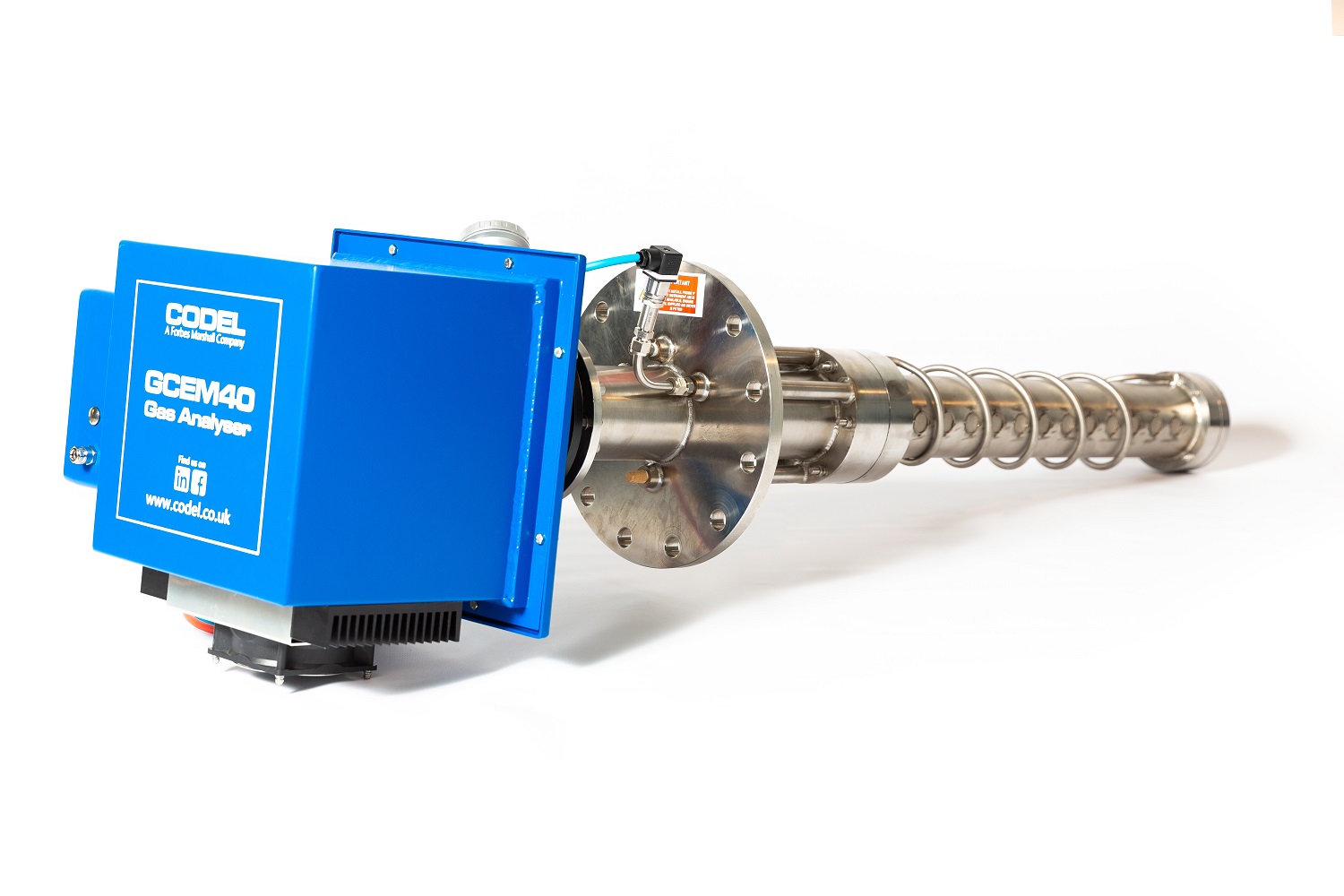
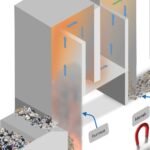
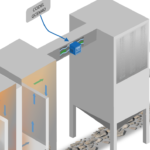
Monitoring SO₂ and HCl levels at the Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD) system inlet is crucial for precise sorbent management. By optimizing sorbent dosage, operators minimize excess usage, leading to cost savings and improved environmental sustainability. This proactive approach boosts operational efficiency and reduces unnecessary expenses. Instruments like the CODEL GCEM 40 enable accurate and reliable monitoring for optimal results.
Operational Efficiency
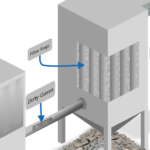
Efficient absorbers are critical for Waste to Energy (WtE) plants. Precise process control, including accurate fuel mixing and real-time measurements, ensures maximum absorber performance. By blending fuels to generate HCl at levels that boost SO₂ absorption in scrubbers, WtE plants achieve greater efficiency and maintain compliance with environmental standards.
Addressing Environmental Concerns
Acidic gas emissions, such as HCl and SO₂, are significant environmental challenges in WtE operations. Absorbers using alkaline substances like lime or sodium bicarbonate neutralize these gases, converting them into less harmful compounds. This process is vital for meeting strict environmental regulations, safeguarding air quality, and protecting public health.
Why Use CODEL for Monitoring Your Energy From Waste Operations
At CODEL, we specialize in supporting Waste-to-Energy (WtE) plants with advanced emissions monitoring solutions tailored to meet the unique demands of energy recovery operations. Our systems, like the CODEL GCEM 40, provide precise real-time measurements of critical pollutants such as SO₂ and HCl, enabling optimized sorbent management, reduced operational costs, and improved process efficiency.
By ensuring compliance with strict environmental regulations, CODEL helps WtE plants address key challenges like acidic gas emissions while promoting sustainable energy production. With our reliable monitoring technology, your plant can achieve greater operational performance, safeguard air quality, and contribute to a cleaner, healthier environment.
Download our EFW Specific brochure here:
Suitable Products
The GCEM40 analyser is an in-situ device which is cost-effective, low maintenance and designed both for process control and emissions monitoring.
CO, NOx, SO2, HCl, CH4, CO2 & H2O
The GCEM40E hot extractive multi-channel gas analyser is CODEL’s industry-proven continuous emissions monitor for difficult applications
CO, NOx, SO2, HCl, CH4, CO2 & H2O
Ask a question
For further information on any of our products, please complete our enquiry form and a member of staff will respond as soon as possible.
You can also call: +44(0)1629 814351